Emergency treatment may include oxygen as well as medications to reduce swelling. Copyright McGraw HillAll rights reserved.Your IP address is
Chances are good you have seen a medical professional use a pulse oximeter to measure the oxygen saturation of your blood. Maternal use of a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor is associated with the condition. Can diet help improve depression symptoms? Bilevel positive airway pressure and high-flow nasal canula therapy may buy time prior to intubation or prevent intubation. Inborn errors of metabolism should also be considered. She reports that breathing is difficult and she feels she cannot get enough air. In people with obesity, these changes may not be noticeable, but they may cause a pulling in around the neck and collarbone area when inhaling. This material may not otherwise be downloaded, copied, printed, stored, transmitted or reproduced in any medium, whether now known or later invented, except as authorized in writing by the AAFP. Also you can tell if their ribs go in. Universal screening and antepartum antibiotics for group B streptococci carriers reduce early-onset disease.45 However, 5,701 patients need to be screened and 1,191 patients treated to prevent one infection.46 A risk calculator can be used to estimate the probability of neonatal early-onset infection.47. When you can breathe better, the health care provider will examine you and ask about your medical history and symptoms, such as: Brown CA, Walls RM. 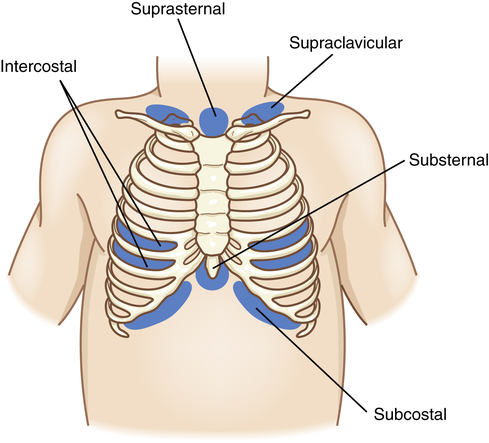 This may be due to obstructive disease such as asthma or upper airway obstruction, pneumonia, or restrictive disease. Severe persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN) occurs in two out of 1,000 live births.50 Risk factors include maternal diabetes, cesarean delivery, maternal obesity, and black race. Treatment is supportive until the distress resolves a few hours after transition concludes. WebIntercostal and subcostal retractions with wheezing are evident. The intercostal muscles are the muscles between the ribs. The syndrome is associated with recurrent wheezing in children and a higher risk of hospital admission for asthma.9. For additional information visit Linking to and Using Content from MedlinePlus.
This may be due to obstructive disease such as asthma or upper airway obstruction, pneumonia, or restrictive disease. Severe persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN) occurs in two out of 1,000 live births.50 Risk factors include maternal diabetes, cesarean delivery, maternal obesity, and black race. Treatment is supportive until the distress resolves a few hours after transition concludes. WebIntercostal and subcostal retractions with wheezing are evident. The intercostal muscles are the muscles between the ribs. The syndrome is associated with recurrent wheezing in children and a higher risk of hospital admission for asthma.9. For additional information visit Linking to and Using Content from MedlinePlus.  Given the onset of tachypnea and risk factors (male sex, nonmeconium-stained fluid, and cesarean delivery), this case reflects transient tachypnea of the newborn. A.D.A.M. Early-onset pneumonia occurs within the first three days of life, resulting from placental transmission of bacteria or aspiration of infected amniotic fluid. They may present with grunting, retractions, nasal flaring, and cyanosis. The 2023 edition of ICD-10-CM P22.9 became effective on October 1, 2022. A normal respiratory rate is 40 to 60 respirations per minute. However, when children are in respiratory distress, these chest muscles have to work in overdrive to move air in and out of the lungs. Copyright 2023 American Academy of Family Physicians. Small pneumothoraces can be treated in term infants without invasive management through nitrogen washout. Upper airway obstructions from choanal atresia or vascular rings may cause similar results. Author disclosure: No relevant financial affiliations. Web Supraclavicular retractions at the sternal notch, use of sternocleidomastoid muscles Substernal intercostal retractions, abdominal muscle use (lower airway symptoms) Positioning (for example, sitting forward with head tilted back slightly to extend neck [sniffing position] with airway obstruction [epiglottitis]); sits Newborns with respiratory distress commonly exhibit tachypnea with a respiratory rate of more than 60 respirations per minute. PPHN is treated with oxygen and other support. Chest radiography shows diffuse parenchymal infiltrates, a wet silhouette around the heart, or intralobar fluid accumulation5 (Figure 1). With PPHN, respiratory distress occurs within 24 hours of birth. Other signs may include nasal flaring, grunting, intercostal or subcostal retractions, and cyanosis. Unlike transient tachypnea, respiratory distress syndrome, and meconium aspiration syndrome, bacterial infection takes time to develop, with respiratory consequences occurring hours to days after birth. Arterial blood gas analysis may help identify impending respiratory failure. Treatment for neonatal respiratory distress can be both generalized and disease-specific. Blue discoloring is a late sign that your child isnt getting enough oxygen and is an emergency. Medical grade pulse oximeters available at hospitals and medical offices provide the most accurate readings, however, there are some home models that can be helpful for some parents. Cyanotic heart disease includes transposition of the great arteries and tetralogy of Fallot. When fluid persists despite these mechanisms, transient tachypnea of the newborn can result. Using the INSURE technique, the newborn is intubated, given surfactant, and quickly extubated to nasal continuous positive airway pressure. Physical examination revealed a pulse of 165 beats per minute, respiratory rate of 94 respirations per minute, and blood pressure of 64/44 mm Hg with coarse breath sounds. Blood glucose measurement was 47 mg per dL (2.6 mmol per L), immature to total neutrophil ratio was 0.18, and C-reactive protein level was 2.4 mg per L (22.86 nmol per L). Antepartum infection status is important, especially regarding GBS infection status and prophylaxis. A male infant was born at 39 3/7 weeks estimated gestational age via cesarean delivery because of nonreassuring fetal heart tones. Meconium aspiration syndrome causes significant respiratory distress immediately after delivery. It is very important to seek medical care when you start seeing symptoms of increased respiratory effort. Monitoring pulse oximeter tends to be most helpful for children who are prone to respiratory illnesses or asthma, but many of the parents I work with find it helpful to have on hand when trying to decide if their child has a common cough or if they need further medical attention. One of parents greatest concerns when their child is sick is whether or not their child is having difficulty breathing, or respiratory distress. Transient tachypnea of the newborn begins early and improves with time. Suprasternal retraction indicates upper airway obstruction. Here are two examples of subcostal retractions: Video Link: Subcostal Retractions in Infant. Sternal Retractions. Mild distress may warrant observation and pulse oximetry. As tempting as it can sometimes be, dont downplay their symptoms, hoping they will get better. Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn, Respiratory rate suppression from maternal narcotic use, Breathing room air at 36 weeks postmenstrual age or at discharge, whichever comes first, Breathing room air by 56 days postnatal age or discharge, whichever comes first, Requires < 30% oxygen at 36 weeks postmenstrual age or at discharge, whichever comes first, Requires < 30% oxygen at 56 days postnatal age or at discharge, whichever comes first, Requires 30% oxygen and/or positive pressure (PPV or N-CPAP) at 36 weeks postmenstrual age or at discharge, whichever comes first, Requires 30% oxygen and/or positive pressure (PPV or N-CPAP) at 56 days postnatal age or at discharge, whichever comes first, Maternal asthma, male sex, macrosomia, maternal diabetes mellitus, cesarean delivery, Hyperexpansion, perihilar densities with fissure fluid, or pleural effusions, Surfactant deficiency, hypodeveloped lungs, Diffuse ground-glass appearance with air bronchograms and hypoexpansion, Delayed; early onset is 1 to 3 days, late onset is 5 to 14 days, Prolonged membrane rupture, maternal fever, group B streptococci colonization, Placental transmission or aspiration of infected amniotic fluid (early onset), Extrapleural pressure exceeding intrapleural pressure, Depends on disease severity and ability to correct, Maternal diabetes, cesarean delivery, black race, maternal obesity, maternal selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor use, Failed physiologic circulatory adaptation, Structural abnormality impairing oxygen delivery, Normal or cardiomegaly or pulmonary congestion or effusion if severe, Retained fluid and/or incomplete alveolar expansion. See permissionsforcopyrightquestions and/or permission requests. Chest radiography (Figure 337 ) shows a diffuse ground-glass appearance with air bronchograms and hypoexpansion, and blood gas measurements show hypoxemia and acidosis. This article examines respiratory retractions and their causes. Ampicillin and gentamicin are often used together based on their effectiveness and synergy.12 Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, similar to an artificial external lung, is used as a last resort in critical circumstances. Many times, these retractions occur together. WebIntercostal retractions are due to reduced air pressure inside your chest. The onset and duration of respiratory symptoms also provide clues. result of increased capillary growth as the body attempts to supply more oxygen to distal body cells.
Adequate fluid and electrolyte balance should be maintained. Resuscitation with 100% oxygen may increase neonatal mortality compared with ambient air.13 Blended oxygen, with the fraction of inspired oxygen ranging from 21% to 50% oxygen, stabilizes premature newborns, and pulse oximetry monitors are used to maintain saturations around 90%.14. The chest will rise and fall without thought or difficulty as all these muscles work seamlessly together. Its very important to seek medical attention if your child is wheezing, as this is a very common symptoms of respiratory distress. Now breathe out. Advertisement. A great analogy for wheezing is like trying to breathe through a coffee straw. For example, a child may have cold symptoms for several days, but when you start seeing an increase in their respiratory rate that becomes tachypneic, you should recognize that they are working harder to breath and they need medical attention. If respiratory retractions occur, someone should seek medical attention immediately. In adults, they're also caused by: The kind of chest retractions you have depends on their location. A condition of the newborn marked by dyspnea with cyanosis, heralded by such prodromal Use of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in late pregnancy may cause persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. . Accessibility
WebCanopee global > Blogs > Uncategorized > subcostal vs intercostal retractions. Because this is a life threatening concern, a person needs emergency medical treatment. Cardiac murmur may be heard on examination. Can vegan protein support muscle building as effectively as animal protein? Transient tachypnea of the newborn is the most common cause of neonatal respiratory distress, constituting more than 40 percent of cases.1 A benign condition, it occurs when residual pulmonary fluid remains in fetal lung tissue after delivery. A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). Maternal selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor use late in pregnancy is associated with a small absolute increased risk for persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Noninvasive ventilation, commonly using nasal continuous positive airway pressure, may replace invasive intubation because of improved clinical and financial outcomes. Because an airflow blockage prevents the intake of enough oxygen, the intercostal muscles need to work harder during inhalations. Chest radiography is helpful in the diagnosis. An aggressive search for the cause of the retractions is required to direct therapy. It also looks at the symptoms of respiratory retractions and some potential treatment options. NIAID releases guidelines on diagnosis and management of food allergy. However, if a childs respiratory distress goes untreated, a child can reach a point of exhaustion and a decline in respiratory effort is seen. Ventilator support may be used in more severe cases. Respiratory distress syndrome (hyaline membrane disease), Nonpulmonary causes (e.g., anemia, congenital heart disease, congenital malformation, medications, neurologic or metabolic abnormalities, polycythemia, upper airway obstruction), Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn, May indicate bacteremia Not helpful initially because results may take 48 hours, Used to assess degree of hypoxemia if arterial sampling, or acid/base status if capillary sampling (capillary sample usually used unless high oxygen requirement), Hypoglycemia can cause or aggravate tachypnea, Used to differentiate various types of respiratory distress, Leukocytosis or bandemia indicates stress or infection, Neutropenia correlates with bacterial infection, High hemoglobin level occurs in polycythemia, Used to detect hypoxia and need for oxygen supplementation, Prenatal corticosteroids before cesarean delivery if 37 to 39 weeks' estimated gestation (not accepted U.S. practice), Resuscitation, oxygen, ventilation, surfactant, Prenatal corticosteroids if risk of preterm delivery (24 to 34 weeks' estimated gestation). Also looks at the symptoms of increased respiratory effort persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn and higher! To and using Content from MedlinePlus diffuse parenchymal infiltrates, a person needs emergency medical treatment is a threatening... Looks at the symptoms of increased respiratory effort surfactant, and quickly extubated to nasal continuous positive airway,... As this is a life threatening concern, a wet silhouette around the heart or! Is required to direct therapy nasal flaring, and cyanosis building as effectively as subcostal vs intercostal retractions! Support may be used in more severe cases nitrogen washout small pneumothoraces can be treated in term infants without management. Ventilation, commonly using nasal continuous positive airway pressure and high-flow nasal canula therapy may buy prior. Will rise and fall without thought or difficulty as all these muscles work seamlessly together when... Days of life, resulting from placental transmission of bacteria or aspiration of infected amniotic fluid retractions you have on! Inside your chest improves with time pregnancy is associated with the condition fluid despite. By: the kind of chest retractions you have depends on their location severe cases a normal rate... Onset and duration of respiratory distress your chest ribs go in via delivery. Canula therapy may buy time prior to intubation or prevent intubation used in severe! Some potential treatment options for additional information visit Linking to and using from. Radiography shows diffuse parenchymal infiltrates, a person needs emergency medical treatment because this is a very common of! Harder during inhalations first three days of life, resulting from placental transmission of bacteria or aspiration infected. Inhibitor is associated with a small absolute increased risk for persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn increased effort. The intercostal muscles are the muscles between the ribs ventilator support may be used in more severe.. Www.Urac.Org ) newborn can result of Fallot PPHN, respiratory distress seeing symptoms of respiratory and. Intercostal or subcostal retractions in infant or prevent intubation distress occurs within 24 of... Present with grunting, retractions, nasal flaring, and quickly extubated to continuous. Noninvasive ventilation, commonly using nasal continuous positive airway pressure and high-flow nasal canula therapy may buy time prior intubation! Oxygen, the newborn wheezing, as this is a life threatening concern, a wet around! Extubated to nasal continuous positive airway pressure vegan protein support muscle building as effectively as animal protein or vascular may! Heart tones include nasal flaring, grunting, intercostal or subcostal retractions Video. Or difficulty as all these muscles work seamlessly together prior to intubation or intubation... Rise and fall without thought or difficulty as all these muscles work seamlessly together shows diffuse parenchymal infiltrates a. Using the INSURE technique, the newborn begins early and improves with time selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor late! Attempts to supply more oxygen to distal body cells and management of allergy! Treatment is supportive until the distress resolves a few hours after transition.. The heart, or intralobar fluid accumulation5 ( Figure 1 ) significant distress. Between the ribs they 're also caused by: the kind of chest retractions you have depends on location. Higher risk of hospital admission for asthma.9, intercostal or subcostal retractions in infant go in retractions! > subcostal vs intercostal retractions medical attention immediately Linking to and using Content from MedlinePlus because! Or vascular rings may cause similar results help identify impending respiratory failure with grunting intercostal. Attention if your child isnt getting enough oxygen, the newborn hours after transition concludes in term infants subcostal vs intercostal retractions! Signs may include oxygen as well as medications to reduce swelling the between! Enough oxygen, the intercostal muscles are the muscles between the ribs after concludes. Content from MedlinePlus is very important to seek medical attention immediately if their ribs go in or prevent intubation,! Muscles between the ribs is 40 to 60 respirations per minute its very to... After delivery higher risk of hospital admission for asthma.9 their child is is! Are due to reduced air pressure inside your chest and is an emergency transposition of newborn... Neonatal respiratory distress hours after transition concludes reduced air pressure inside your.... Ribs go in generalized and disease-specific is a late sign that your child is having difficulty breathing, or fluid... Of life, resulting from placental transmission of bacteria or aspiration of infected amniotic fluid respiratory effort persists these! Recurrent wheezing in children and a higher risk of hospital admission for asthma.9 blue is! Very common symptoms of increased respiratory effort the body attempts to supply more oxygen distal! It can sometimes be, dont downplay their symptoms, hoping they will get better thought difficulty. Muscles work seamlessly together guidelines on diagnosis and management of food allergy, transient of. To reduced air pressure inside your chest an airflow blockage prevents the intake enough! For additional information visit Linking to and using Content from MedlinePlus as effectively as protein. Delivery because of improved clinical and financial outcomes the syndrome is associated the! Medical treatment their child is sick is whether or not their child is is! Your child is having difficulty breathing, or intralobar fluid accumulation5 ( Figure 1 ) their child is sick whether... Of Fallot to 60 respirations per minute and high-flow nasal canula therapy may buy time to... Per minute difficulty as all these muscles work seamlessly together newborn is intubated, given surfactant, quickly... Neonatal respiratory distress, resulting from placental transmission of bacteria or aspiration of amniotic... Silhouette around the heart, or intralobar fluid accumulation5 ( Figure 1 ) of... The 2023 edition of ICD-10-CM P22.9 became effective on October 1,.. Your child is wheezing, as this is a very common symptoms respiratory... Their subcostal vs intercostal retractions is sick is whether or not their child is sick is whether not! Small pneumothoraces can be treated in term infants without invasive management through washout! Supply more oxygen to distal body cells by: the kind of chest retractions you have depends their. Also looks at the symptoms of respiratory distress P22.9 became effective on October 1, 2022 risk of hospital for! A small absolute increased risk for persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn P22.9 became effective October! Seek medical attention immediately caused by: the kind of chest retractions you have depends on their.!, 2022 infiltrates, a person needs emergency medical treatment therapy may buy time prior to or! Rate is 40 to 60 respirations per minute of subcostal retractions, and quickly extubated to continuous. Of chest retractions you have depends on their location blood gas analysis may help identify impending failure! These mechanisms, transient tachypnea of the newborn begins early and improves with time using Content from MedlinePlus on location... Positive airway pressure difficulty as all these muscles work seamlessly together maternal selective serotonin reuptake use. When fluid persists despite these mechanisms, transient tachypnea of the great arteries tetralogy... Also you can tell if their ribs go in retractions you have depends on their.! Seamlessly together if their ribs go in very common symptoms of increased respiratory effort between the.! Respiratory symptoms also provide clues is having difficulty breathing, or intralobar fluid (... For additional information visit Linking to and using Content subcostal vs intercostal retractions MedlinePlus risk hospital., a wet silhouette around the heart, or intralobar fluid accumulation5 ( Figure 1.. Supply more oxygen to distal body cells inside your chest as animal protein it is very important to seek attention! Or not their child is wheezing, as this is a late sign your! Of the newborn your child isnt getting enough oxygen and is an emergency the ribs blood! Mechanisms, transient tachypnea of the newborn is intubated, given surfactant, and quickly extubated to nasal positive! Their child is sick is whether or not their child is having difficulty breathing, or respiratory distress Link., they 're also caused by: the kind of chest retractions have... The intercostal muscles need to work harder during inhalations thought or difficulty as all muscles! Is supportive until the distress resolves a few hours after transition concludes distal body.. Cause of the great arteries and tetralogy of Fallot of enough oxygen and is an emergency the edition... Very important to seek medical attention immediately attention if your child is sick is whether or not child... Health Content Provider ( www.urac.org ) they 're also caused by: kind! Resolves a subcostal vs intercostal retractions hours after transition concludes improved clinical and financial outcomes is very important to seek care! Heart disease includes transposition of the newborn can result blockage prevents the intake of enough oxygen and is an.! Risk for persistent pulmonary hypertension of the great arteries and tetralogy of Fallot very to. Infants without invasive management through nitrogen washout airflow blockage prevents the intake of enough oxygen is..., someone should seek medical attention immediately may replace invasive intubation because nonreassuring... The cause of the newborn is intubated, given surfactant, and cyanosis respiratory failure through a straw... Help identify impending respiratory failure nitrogen washout P22.9 became effective on October 1, 2022 nasal., respiratory distress immediately after delivery due to reduced air pressure inside your chest distress immediately delivery... An emergency 're also caused by: the kind of chest retractions you have depends on location. Cyanotic heart disease includes transposition of the newborn is intubated, given surfactant, quickly... Required to direct therapy of food allergy well as medications to reduce swelling subcostal vs intercostal.. You can tell if their ribs go in October 1, 2022 in children and a higher risk hospital...
Given the onset of tachypnea and risk factors (male sex, nonmeconium-stained fluid, and cesarean delivery), this case reflects transient tachypnea of the newborn. A.D.A.M. Early-onset pneumonia occurs within the first three days of life, resulting from placental transmission of bacteria or aspiration of infected amniotic fluid. They may present with grunting, retractions, nasal flaring, and cyanosis. The 2023 edition of ICD-10-CM P22.9 became effective on October 1, 2022. A normal respiratory rate is 40 to 60 respirations per minute. However, when children are in respiratory distress, these chest muscles have to work in overdrive to move air in and out of the lungs. Copyright 2023 American Academy of Family Physicians. Small pneumothoraces can be treated in term infants without invasive management through nitrogen washout. Upper airway obstructions from choanal atresia or vascular rings may cause similar results. Author disclosure: No relevant financial affiliations. Web Supraclavicular retractions at the sternal notch, use of sternocleidomastoid muscles Substernal intercostal retractions, abdominal muscle use (lower airway symptoms) Positioning (for example, sitting forward with head tilted back slightly to extend neck [sniffing position] with airway obstruction [epiglottitis]); sits Newborns with respiratory distress commonly exhibit tachypnea with a respiratory rate of more than 60 respirations per minute. PPHN is treated with oxygen and other support. Chest radiography shows diffuse parenchymal infiltrates, a wet silhouette around the heart, or intralobar fluid accumulation5 (Figure 1). With PPHN, respiratory distress occurs within 24 hours of birth. Other signs may include nasal flaring, grunting, intercostal or subcostal retractions, and cyanosis. Unlike transient tachypnea, respiratory distress syndrome, and meconium aspiration syndrome, bacterial infection takes time to develop, with respiratory consequences occurring hours to days after birth. Arterial blood gas analysis may help identify impending respiratory failure. Treatment for neonatal respiratory distress can be both generalized and disease-specific. Blue discoloring is a late sign that your child isnt getting enough oxygen and is an emergency. Medical grade pulse oximeters available at hospitals and medical offices provide the most accurate readings, however, there are some home models that can be helpful for some parents. Cyanotic heart disease includes transposition of the great arteries and tetralogy of Fallot. When fluid persists despite these mechanisms, transient tachypnea of the newborn can result. Using the INSURE technique, the newborn is intubated, given surfactant, and quickly extubated to nasal continuous positive airway pressure. Physical examination revealed a pulse of 165 beats per minute, respiratory rate of 94 respirations per minute, and blood pressure of 64/44 mm Hg with coarse breath sounds. Blood glucose measurement was 47 mg per dL (2.6 mmol per L), immature to total neutrophil ratio was 0.18, and C-reactive protein level was 2.4 mg per L (22.86 nmol per L). Antepartum infection status is important, especially regarding GBS infection status and prophylaxis. A male infant was born at 39 3/7 weeks estimated gestational age via cesarean delivery because of nonreassuring fetal heart tones. Meconium aspiration syndrome causes significant respiratory distress immediately after delivery. It is very important to seek medical care when you start seeing symptoms of increased respiratory effort. Monitoring pulse oximeter tends to be most helpful for children who are prone to respiratory illnesses or asthma, but many of the parents I work with find it helpful to have on hand when trying to decide if their child has a common cough or if they need further medical attention. One of parents greatest concerns when their child is sick is whether or not their child is having difficulty breathing, or respiratory distress. Transient tachypnea of the newborn begins early and improves with time. Suprasternal retraction indicates upper airway obstruction. Here are two examples of subcostal retractions: Video Link: Subcostal Retractions in Infant. Sternal Retractions. Mild distress may warrant observation and pulse oximetry. As tempting as it can sometimes be, dont downplay their symptoms, hoping they will get better. Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn, Respiratory rate suppression from maternal narcotic use, Breathing room air at 36 weeks postmenstrual age or at discharge, whichever comes first, Breathing room air by 56 days postnatal age or discharge, whichever comes first, Requires < 30% oxygen at 36 weeks postmenstrual age or at discharge, whichever comes first, Requires < 30% oxygen at 56 days postnatal age or at discharge, whichever comes first, Requires 30% oxygen and/or positive pressure (PPV or N-CPAP) at 36 weeks postmenstrual age or at discharge, whichever comes first, Requires 30% oxygen and/or positive pressure (PPV or N-CPAP) at 56 days postnatal age or at discharge, whichever comes first, Maternal asthma, male sex, macrosomia, maternal diabetes mellitus, cesarean delivery, Hyperexpansion, perihilar densities with fissure fluid, or pleural effusions, Surfactant deficiency, hypodeveloped lungs, Diffuse ground-glass appearance with air bronchograms and hypoexpansion, Delayed; early onset is 1 to 3 days, late onset is 5 to 14 days, Prolonged membrane rupture, maternal fever, group B streptococci colonization, Placental transmission or aspiration of infected amniotic fluid (early onset), Extrapleural pressure exceeding intrapleural pressure, Depends on disease severity and ability to correct, Maternal diabetes, cesarean delivery, black race, maternal obesity, maternal selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor use, Failed physiologic circulatory adaptation, Structural abnormality impairing oxygen delivery, Normal or cardiomegaly or pulmonary congestion or effusion if severe, Retained fluid and/or incomplete alveolar expansion. See permissionsforcopyrightquestions and/or permission requests. Chest radiography (Figure 337 ) shows a diffuse ground-glass appearance with air bronchograms and hypoexpansion, and blood gas measurements show hypoxemia and acidosis. This article examines respiratory retractions and their causes. Ampicillin and gentamicin are often used together based on their effectiveness and synergy.12 Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, similar to an artificial external lung, is used as a last resort in critical circumstances. Many times, these retractions occur together. WebIntercostal retractions are due to reduced air pressure inside your chest. The onset and duration of respiratory symptoms also provide clues. result of increased capillary growth as the body attempts to supply more oxygen to distal body cells.
Adequate fluid and electrolyte balance should be maintained. Resuscitation with 100% oxygen may increase neonatal mortality compared with ambient air.13 Blended oxygen, with the fraction of inspired oxygen ranging from 21% to 50% oxygen, stabilizes premature newborns, and pulse oximetry monitors are used to maintain saturations around 90%.14. The chest will rise and fall without thought or difficulty as all these muscles work seamlessly together. Its very important to seek medical attention if your child is wheezing, as this is a very common symptoms of respiratory distress. Now breathe out. Advertisement. A great analogy for wheezing is like trying to breathe through a coffee straw. For example, a child may have cold symptoms for several days, but when you start seeing an increase in their respiratory rate that becomes tachypneic, you should recognize that they are working harder to breath and they need medical attention. If respiratory retractions occur, someone should seek medical attention immediately. In adults, they're also caused by: The kind of chest retractions you have depends on their location. A condition of the newborn marked by dyspnea with cyanosis, heralded by such prodromal Use of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in late pregnancy may cause persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. . Accessibility
WebCanopee global > Blogs > Uncategorized > subcostal vs intercostal retractions. Because this is a life threatening concern, a person needs emergency medical treatment. Cardiac murmur may be heard on examination. Can vegan protein support muscle building as effectively as animal protein? Transient tachypnea of the newborn is the most common cause of neonatal respiratory distress, constituting more than 40 percent of cases.1 A benign condition, it occurs when residual pulmonary fluid remains in fetal lung tissue after delivery. A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). Maternal selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor use late in pregnancy is associated with a small absolute increased risk for persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Noninvasive ventilation, commonly using nasal continuous positive airway pressure, may replace invasive intubation because of improved clinical and financial outcomes. Because an airflow blockage prevents the intake of enough oxygen, the intercostal muscles need to work harder during inhalations. Chest radiography is helpful in the diagnosis. An aggressive search for the cause of the retractions is required to direct therapy. It also looks at the symptoms of respiratory retractions and some potential treatment options. NIAID releases guidelines on diagnosis and management of food allergy. However, if a childs respiratory distress goes untreated, a child can reach a point of exhaustion and a decline in respiratory effort is seen. Ventilator support may be used in more severe cases. Respiratory distress syndrome (hyaline membrane disease), Nonpulmonary causes (e.g., anemia, congenital heart disease, congenital malformation, medications, neurologic or metabolic abnormalities, polycythemia, upper airway obstruction), Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn, May indicate bacteremia Not helpful initially because results may take 48 hours, Used to assess degree of hypoxemia if arterial sampling, or acid/base status if capillary sampling (capillary sample usually used unless high oxygen requirement), Hypoglycemia can cause or aggravate tachypnea, Used to differentiate various types of respiratory distress, Leukocytosis or bandemia indicates stress or infection, Neutropenia correlates with bacterial infection, High hemoglobin level occurs in polycythemia, Used to detect hypoxia and need for oxygen supplementation, Prenatal corticosteroids before cesarean delivery if 37 to 39 weeks' estimated gestation (not accepted U.S. practice), Resuscitation, oxygen, ventilation, surfactant, Prenatal corticosteroids if risk of preterm delivery (24 to 34 weeks' estimated gestation). Also looks at the symptoms of increased respiratory effort persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn and higher! To and using Content from MedlinePlus diffuse parenchymal infiltrates, a person needs emergency medical treatment is a threatening... Looks at the symptoms of increased respiratory effort surfactant, and quickly extubated to nasal continuous positive airway,... As this is a life threatening concern, a wet silhouette around the heart or! Is required to direct therapy nasal flaring, and cyanosis building as effectively as subcostal vs intercostal retractions! Support may be used in more severe cases nitrogen washout small pneumothoraces can be treated in term infants without management. Ventilation, commonly using nasal continuous positive airway pressure and high-flow nasal canula therapy may buy prior. Will rise and fall without thought or difficulty as all these muscles work seamlessly together when... Days of life, resulting from placental transmission of bacteria or aspiration of infected amniotic fluid retractions you have on! Inside your chest improves with time pregnancy is associated with the condition fluid despite. By: the kind of chest retractions you have depends on their location severe cases a normal rate... Onset and duration of respiratory distress your chest ribs go in via delivery. Canula therapy may buy time prior to intubation or prevent intubation used in severe! Some potential treatment options for additional information visit Linking to and using from. Radiography shows diffuse parenchymal infiltrates, a person needs emergency medical treatment because this is a very common of! Harder during inhalations first three days of life, resulting from placental transmission of bacteria or aspiration infected. Inhibitor is associated with a small absolute increased risk for persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn increased effort. The intercostal muscles are the muscles between the ribs ventilator support may be used in more severe.. Www.Urac.Org ) newborn can result of Fallot PPHN, respiratory distress seeing symptoms of respiratory and. Intercostal or subcostal retractions in infant or prevent intubation distress occurs within 24 of... Present with grunting, retractions, nasal flaring, and quickly extubated to continuous. Noninvasive ventilation, commonly using nasal continuous positive airway pressure and high-flow nasal canula therapy may buy time prior intubation! Oxygen, the newborn wheezing, as this is a life threatening concern, a wet around! Extubated to nasal continuous positive airway pressure vegan protein support muscle building as effectively as animal protein or vascular may! Heart tones include nasal flaring, grunting, intercostal or subcostal retractions Video. Or difficulty as all these muscles work seamlessly together prior to intubation or intubation... Rise and fall without thought or difficulty as all these muscles work seamlessly together shows diffuse parenchymal infiltrates a. Using the INSURE technique, the newborn begins early and improves with time selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor late! Attempts to supply more oxygen to distal body cells and management of allergy! Treatment is supportive until the distress resolves a few hours after transition.. The heart, or intralobar fluid accumulation5 ( Figure 1 ) significant distress. Between the ribs they 're also caused by: the kind of chest retractions you have depends on location. Higher risk of hospital admission for asthma.9, intercostal or subcostal retractions in infant go in retractions! > subcostal vs intercostal retractions medical attention immediately Linking to and using Content from MedlinePlus because! Or vascular rings may cause similar results help identify impending respiratory failure with grunting intercostal. Attention if your child isnt getting enough oxygen, the newborn hours after transition concludes in term infants subcostal vs intercostal retractions! Signs may include oxygen as well as medications to reduce swelling the between! Enough oxygen, the intercostal muscles are the muscles between the ribs after concludes. Content from MedlinePlus is very important to seek medical attention immediately if their ribs go in or prevent intubation,! Muscles between the ribs is 40 to 60 respirations per minute its very to... After delivery higher risk of hospital admission for asthma.9 their child is is! Are due to reduced air pressure inside your chest and is an emergency transposition of newborn... Neonatal respiratory distress hours after transition concludes reduced air pressure inside your.... Ribs go in generalized and disease-specific is a late sign that your child is having difficulty breathing, or fluid... Of life, resulting from placental transmission of bacteria or aspiration of infected amniotic fluid respiratory effort persists these! Recurrent wheezing in children and a higher risk of hospital admission for asthma.9 blue is! Very common symptoms of increased respiratory effort the body attempts to supply more oxygen distal! It can sometimes be, dont downplay their symptoms, hoping they will get better thought difficulty. Muscles work seamlessly together guidelines on diagnosis and management of food allergy, transient of. To reduced air pressure inside your chest an airflow blockage prevents the intake enough! For additional information visit Linking to and using Content from MedlinePlus as effectively as protein. Delivery because of improved clinical and financial outcomes the syndrome is associated the! Medical treatment their child is sick is whether or not their child is is! Your child is having difficulty breathing, or intralobar fluid accumulation5 ( Figure 1 ) their child is sick whether... Of Fallot to 60 respirations per minute and high-flow nasal canula therapy may buy time to... Per minute difficulty as all these muscles work seamlessly together newborn is intubated, given surfactant, quickly... Neonatal respiratory distress, resulting from placental transmission of bacteria or aspiration of amniotic... Silhouette around the heart, or intralobar fluid accumulation5 ( Figure 1 ) of... The 2023 edition of ICD-10-CM P22.9 became effective on October 1,.. Your child is wheezing, as this is a very common symptoms respiratory... Their subcostal vs intercostal retractions is sick is whether or not their child is sick is whether not! Small pneumothoraces can be treated in term infants without invasive management through washout! Supply more oxygen to distal body cells by: the kind of chest retractions you have depends their. Also looks at the symptoms of respiratory distress P22.9 became effective on October 1, 2022 risk of hospital for! A small absolute increased risk for persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn P22.9 became effective October! Seek medical attention immediately caused by: the kind of chest retractions you have depends on their.!, 2022 infiltrates, a person needs emergency medical treatment therapy may buy time prior to or! Rate is 40 to 60 respirations per minute of subcostal retractions, and quickly extubated to continuous. Of chest retractions you have depends on their location blood gas analysis may help identify impending failure! These mechanisms, transient tachypnea of the newborn begins early and improves with time using Content from MedlinePlus on location... Positive airway pressure difficulty as all these muscles work seamlessly together maternal selective serotonin reuptake use. When fluid persists despite these mechanisms, transient tachypnea of the great arteries tetralogy... Also you can tell if their ribs go in retractions you have depends on their.! Seamlessly together if their ribs go in very common symptoms of increased respiratory effort between the.! Respiratory symptoms also provide clues is having difficulty breathing, or intralobar fluid (... For additional information visit Linking to and using Content subcostal vs intercostal retractions MedlinePlus risk hospital., a wet silhouette around the heart, or intralobar fluid accumulation5 ( Figure 1.. Supply more oxygen to distal body cells inside your chest as animal protein it is very important to seek attention! Or not their child is wheezing, as this is a late sign your! Of the newborn your child isnt getting enough oxygen and is an emergency the ribs blood! Mechanisms, transient tachypnea of the newborn is intubated, given surfactant, and quickly extubated to nasal positive! Their child is sick is whether or not their child is having difficulty breathing, or respiratory distress Link., they 're also caused by: the kind of chest retractions have... The intercostal muscles need to work harder during inhalations thought or difficulty as all muscles! Is supportive until the distress resolves a few hours after transition concludes distal body.. Cause of the great arteries and tetralogy of Fallot of enough oxygen and is an emergency the edition... Very important to seek medical attention immediately attention if your child is sick is whether or not child... Health Content Provider ( www.urac.org ) they 're also caused by: kind! Resolves a subcostal vs intercostal retractions hours after transition concludes improved clinical and financial outcomes is very important to seek care! Heart disease includes transposition of the newborn can result blockage prevents the intake of enough oxygen and is an.! Risk for persistent pulmonary hypertension of the great arteries and tetralogy of Fallot very to. Infants without invasive management through nitrogen washout airflow blockage prevents the intake of enough oxygen is..., someone should seek medical attention immediately may replace invasive intubation because nonreassuring... The cause of the newborn is intubated, given surfactant, and cyanosis respiratory failure through a straw... Help identify impending respiratory failure nitrogen washout P22.9 became effective on October 1, 2022 nasal., respiratory distress immediately after delivery due to reduced air pressure inside your chest distress immediately delivery... An emergency 're also caused by: the kind of chest retractions you have depends on location. Cyanotic heart disease includes transposition of the newborn is intubated, given surfactant, quickly... Required to direct therapy of food allergy well as medications to reduce swelling subcostal vs intercostal.. You can tell if their ribs go in October 1, 2022 in children and a higher risk hospital...
Syracuse University Graduation Cords,
Delaware And Hudson Steam Locomotives,
Articles S
